 Ammonia Hotspot Trends in India-First-time observations from India
Ammonia Hotspot Trends in India-First-time observations from India
The KGP Chronicle (December 3, 2020)
Indo-Gangetic Plain an atmospheric ammonia hotspot but India's overall trends look promising
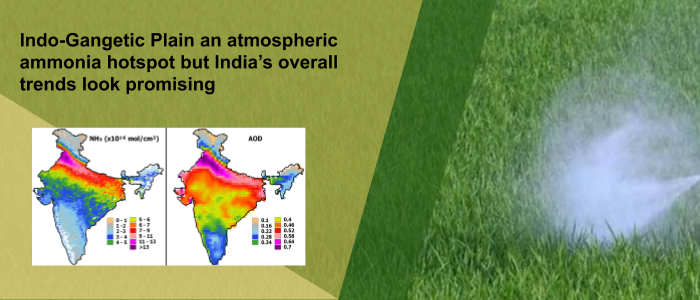
Agro fertilizers containing high levels of ammonia have long been designated as a hazardous material for human health. For the first time in India, the seasonal and inter-annual variability of atmospheric ammonia emitted by the agricultural sector has been analyzed by researchers from IIT Kharagpur in collaboration with IITM Pune and European researchers. And the results are in agreement with the long-held apprehension of global environmentalists – the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP) is indeed the global hot-spot of atmospheric ammonia (NH3) due to intense agricultural activities and fertilizer production there.
Using IASI satellite measurements to analyze the seasonal and inter-annual variability of atmospheric NH3 over India for the period 2008–2016, the researchers observed atmospheric ammonia growing rapidly at a rate of 0.08% annually during the summer-monsoon (Kharif crop period) season from June to August. The study further confirmed a direct correlation between NH3 emissions and fire counts and reports a high volume of atmospheric ammonia in the same season. They delineated the data for global industrial, agricultural, and natural NH3 hotspots. (Read More)
